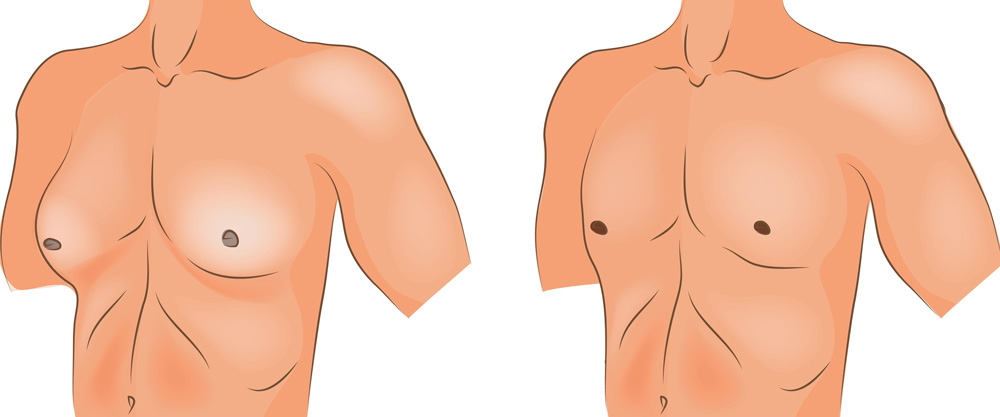
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is the swelling of breast tissue in males or male children, often referred to as “man breasts.” It can affect either one or both breasts. Gynecomastia is commonly observed during puberty and usually resolves on its own with age. Approximately 1 in 3 boys may experience this condition. If gynecomastia is causing significant discomfort, it can be treated with medications or surgical options.
What Are the Symptoms of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can cause enlarged breasts that feel rubbery or firm. Swelling typically starts beneath the nipple and extends to the breast area, and sometimes sensitivity may be experienced. Gynecomastia can lead to sagging of the breasts and stretching of the areola (the dark skin surrounding the nipple).
Gynecomastia differs from breast enlargement due to excess body weight, which results from excessive fat in the breasts. Additionally, gynecomastia is different from male breast cancer, which is usually unilateral, does not always involve the areola, and feels hard or solid.
Gynecomastia is generally not a serious health issue, but it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying medical condition and may cause emotional discomfort.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is typically caused by an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone hormones, which can occur after birth, during puberty, and with aging. Hormone-altering medications can also contribute to gynecomastia. These include anabolic steroids, heart medications, antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and some medications used for depression, high blood pressure, stomach ulcers, and prostate cancer. Marijuana and alcohol can also contribute to the growth of breast tissue.
Other factors causing gynecomastia include rare genetic conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome, kidney or liver diseases, or tumors in the testes or adrenal glands. Additionally, excess prolactin production by the pituitary gland, antipsychotic medications, anti-nausea drugs, underactive thyroid, kidney or liver failure, and marijuana use can also lead to gynecomastia.
How Is Gynecomastia Treated?
Gynecomastia often resolves on its own, typically within 6 months to 2 years. If the condition is caused by medication, discontinuing the medication may resolve the issue. If it is due to an underlying medical condition, treating that condition can improve gynecomastia.
For cases where gynecomastia is painful or causes significant self-consciousness, several treatment options are available. Some medications can reduce breast size in men, but they may not be effective for everyone. Another option is surgery to remove either fat tissue or glandular tissue from the breast.
Your doctor may recommend seeing a plastic surgeon to determine if surgery is a suitable option for you. Surgery may not be effective in individuals with significant excess weight and can leave small scars around the areola.
In adolescent boys, it is generally advisable to wait until the development process is complete before considering surgery.



